Event handling in Java explains you how to handle the external events.

Event Handling In Java
In this section you will learn about how to handle events in Java. Events in any programming language specifies the external effects that happens and your application behaves according to that event. For example, an application produce an output when a user inputs some data, or the data received from the network or it may be something else. In Java when you works with the AWT components like button, textbox, etc (except panel, label ) generates an event. This event is handled by the listener. Event listener listens the event generated on components and performs the corresponding action.
In Java event handling may comprised the following four classes :
- Event Sources : Sources for generating an event may be the
components. In Java java.awt.Component specifies the components that may or may
not generate events. These components classes are the subclass of the above
class. These event sources may be the button, combobox, textbox etc.
- Event Classes : Event Classes in Java are the classes
defined for almost all the components that may generate events. These events
classes are named by giving the specific name such as for the component source
button the event class is ActionEvent. Following are the list of Event Classes :
- ActionEvent : Button, TextField, List, Menu
- WindowEvent : Frame
- ItemEvent : Checkbox, List
- AdjustmentEvent : Scrollbar
- MouseEvent : Mouse
- KeyEvent : Keyboard
- Event Listeners : Event Listeners are the Java interfaces
that provides various methods to use in the implemented class. Listeners listens
the event generated by a component. In Java almost all components has its own
listener that handles the event generated by the component. For example, there
is a Listener named ActionListener handles the events generated from button,
textfield, list, menus.
- Event Adapters : Event Adapters classes are abstract class that provides some methods used for avoiding the heavy coding. Adapter class is defined for the listener that has more than one abstract methods.
Example
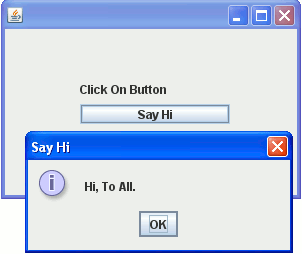
Here I am giving a simple example which will demonstrate you about how to handle an event. In this example we will give a simple example into which you will see how an event generated after clicking on the button is handled. To handle the event you would have to implement a corresponding listener and add the listener on the component i.e. button. Then you have to override the method declared in the listener.
You can add the listener by following ways :
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae)
{
b = (JButton)ae.getSource();
sayHi();
}
});
In the second way you can add listener as follows :
b.addActionListener(this)
publi void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae){
b = (JButton)ae.getSource();
sayHi();
}
EventHandlingExample.java
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class EventHandlingExample implements ActionListener{
JFrame f;
JButton b=new JButton("Say Hi");
public void createUI()
{
f = new JFrame();
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setLayout(null);
JLabel tbLabel = new JLabel("Click On Button");
b.addActionListener(this);
tbLabel.setBounds(75, 50, 100, 20);
b.setBounds(75,75,150,20);
f.add(tbLabel);
f.add(b);
f.setVisible(true);
f.setSize(300,200);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
EventHandlingExample dd = new EventHandlingExample();
dd.createUI();
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
b = (JButton)e.getSource();
sayHi();
}
public void sayHi()
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(f, "Hi, To All.", "Say Hi", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
}
}
Output :
When you will execute the above example you will get the output as follows :