Hibernate 4 One to One Mapping using Annotation
In this section, you will learn how to do one to one mapping in Hibernate using Annotation.
In, One to One mapping the record of one table have only one related record in the other table. For example , in the below example, each record of workerdetail table have only one related record in worker table. In other words, one address in the workerdetail table is related to only one employee or worker in the worker table.
EXAMPLE
In the given below example we will insert the data in two table in just one go. Both the table worker and workerdetail is attached with each other through foreign key worker_id field. In the below example, hibernate one to one mapping is done through annotation.
Previously we need to map the two tables through XML configuration file but using annotation you can directly do that in the model class of database table. For example we did the mapping work in Worker.java and WorkerDetail.java class. In ManageWorker.java class, we insert the values in two tables worker & workerdetail in one go using Hibernate One to One mapping.
The project structure and jar file used is given below :
The sql query used to create the tables worker and workerdetail is given below :
CREATE TABLE `worker` ( `worker_id` bigint(10) NOT NULL auto_increment, `firstname` varchar(50) default NULL, `lastname` varchar(50) default NULL, `birth_date` date NOT NULL, `cell_phone` varchar(15) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`worker_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 CREATE TABLE `workerdetail` ( `worker_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL auto_increment, `street` varchar(50) default NULL, `city` varchar(50) default NULL, `state` varchar(50) default NULL, `country` varchar(50) default NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`worker_id`), CONSTRAINT `FK_workerdetail` FOREIGN KEY (`worker_id`) REFERENCES `worker` (`worker_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1
CODE
hibernate.cfg.xml ( /src/hibernate.cfg.xml )
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- Database connection settings --> <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://192.168.10.13:3306/anky</property> <property name="connection.username">root</property> <property name="connection.password">root</property> <property name="connection.pool_size">1</property> <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <property name="current_session_context_class">thread</property> <property name="cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.NoCacheProvider</property> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">validate</property> <mapping class="net.roseindia.WorkerDetail"/> <mapping class="net.roseindia.Worker"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
Worker.java ( /src/net/roseindia/Worker.java )
package net.roseindia;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "worker")
public class Worker {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "worker_id")
private Long workerId;
@Column(name = "firstname")
private String firstname;
@Column(name = "lastname")
private String lastname;
@Column(name = "birth_date")
private Date birthDate;
@Column(name = "cell_phone")
private String cellphone;
@OneToOne(mappedBy = "worker", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private WorkerDetail workerDetail;
public Worker() {
}
public Worker(String firstname, String lastname, Date birthdate,
String phone) {
this.firstname = firstname;
this.lastname = lastname;
this.birthDate = birthdate;
this.cellphone = phone;
}
public Long getWorkerId() {
return workerId;
}
public void setWorkerId(Long workerId) {
this.workerId = workerId;
}
public String getFirstname() {
return firstname;
}
public void setFirstname(String firstname) {
this.firstname = firstname;
}
public String getLastname() {
return lastname;
}
public void setLastname(String lastname) {
this.lastname = lastname;
}
public Date getBirthDate() {
return birthDate;
}
public void setBirthDate(Date birthDate) {
this.birthDate = birthDate;
}
public String getCellphone() {
return cellphone;
}
public void setCellphone(String cellphone) {
this.cellphone = cellphone;
}
public WorkerDetail getWorkerDetail() {
return workerDetail;
}
public void setWorkerDetail(WorkerDetail workerDetail) {
this.workerDetail = workerDetail;
}
}
WorkerDetail.java( /src/net/roseindia/WorkerDetail.java )
package net.roseindia;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.PrimaryKeyJoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Parameter;
@Entity
@Table(name="workerdetail")
public class WorkerDetail {
@Id
@Column(name="worker_id", unique=true, nullable=false)
@GeneratedValue(generator="gen")
@GenericGenerator(name="gen", strategy="foreign", parameters=@Parameter(name="property", value="worker"))
private Long workerId;
@Column(name="street")
private String street;
@Column(name="city")
private String city;
@Column(name="state")
private String state;
@Column(name="country")
private String country;
@OneToOne
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn
private Worker worker;
public WorkerDetail() {
}
public WorkerDetail(String street, String city, String state, String country) {
this.street = street;
this.city = city;
this.state = state;
this.country = country;
}
public Long getWorkerId() {
return workerId;
}
public void setWorkerId(Long workerId) {
this.workerId = workerId;
}
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public Worker getWorker() {
return worker;
}
public void setWorker(Worker worker) {
this.worker = worker;
}
}
ManageWorker.java ( /src/net/roseindia/ManageWorker.java )
package net.roseindia;
import java.util.Date;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
public class ManageWorker {
private static SessionFactory sf;
private static ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.configure();
serviceRegistry = new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(
configuration.getProperties()).buildServiceRegistry();
sf = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
System.err.println("Failed to create sessionFactory object." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
System.out.println("Example : Hibernate One to One Mapping using Annotation ");
Session session = sf.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
WorkerDetail workerDetail = new WorkerDetail("Lake Town", "Kolkata",
"West Bengal", "India");
//For passing Date of birth as String
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date dob=null;
try {
dob = sdf.parse("1987-05-21");
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Worker worker = new Worker("Sushmita", "Dasgupta",dob,
"919595959595");
worker.setWorkerDetail(workerDetail);
workerDetail.setWorker(worker);
session.save(worker);
List<Worker> workerList = session.createQuery("from Worker").list();
for (Worker work1 : workerList) {
System.out.println(work1.getFirstname() + " , "
+ work1.getLastname() + ", "
+ work1.getWorkerDetail().getState());
}
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
OUTPUT
When you execute the above code, you will get the following output in console :
Example : Hibernate One to One Mapping using Annotation Hibernate: insert into worker (birth_date, cell_phone, firstname, lastname) values (?, ?, ?, ?) Hibernate: select worker0_.worker_id as worker1_1_, worker0_.birth_date as birth2_1_, worker0_.cell_phone as cell3_1_, worker0_.firstname as firstname1_, worker0_.lastname as lastname1_ from worker worker0_ Sushmita , Dasgupta, West Bengal Hibernate: insert into workerdetail (city, country, state, street, worker_id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
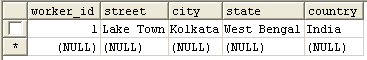
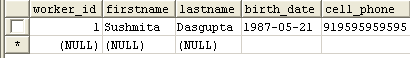
In worker table, you should get the following record :
In workerdetail table you will get the following record :