The class Exception and its subclasses are defined in such a way that an application may generate a condition which might be caught. The Exception class extends the Throwable class. All errors and exception classes are the subclasses of java.lang.Throwable which further extends the java.lang.Object class.

In this section we will discuss about the hierarchy of java.lang.Exception class.
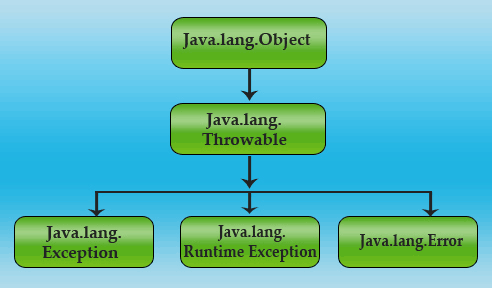
The class Exception and its subclasses are defined in such a way that an application may generate a condition which might be caught. The Exception class extends the Throwable class. All errors and exception classes are the subclasses of java.lang.Throwable which further extends the java.lang.Object class. An image given below explains the hierarchy of java.lang.Exception class.
Constructor Detail
| Exception() | This is a default constructor which creates a new Exception object. It
contains a pre defined message. Syntax : public Exception() |
| Exception(String message) | This constructor creates a new Exception object with the specified message. Syntax : public Exception(String message) |
| Exception(String message, Throwable cause) | This constructor creates a new Exception object with the specified message
and cause. Syntax : public Exception(String message, Throwable cause) |
| Exception(Throwable cause) | This constructor creates a new Exception object with the specified cause. Syntax : public Exception(Throwable cause) |
Method Detail
Methods in this class are inherited from its parent class i.e. java.lang.Throwable and java.lang.Object. Some commonly used methods are as follows :
- getCause() : This method is used to find out the cause of
Throwable or null if the cause is not known or having no existence.
Syntax : public Throwable getCause()
- getMessage() : This method is used to find out the detail
string message of Throwable.
Syntax : public String getMessage()
- printStackTrace() : This method is used to print the
standard error stream.
Syntax : public void printStackTrace() - toString() : This method is used to find out the error
message in a specified format.
- Name of class
- ': " colon followed by a white space.
- result of invoking objects method.
Syntax : public String toString()
