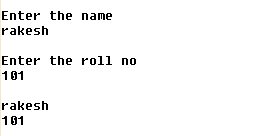Pointer and Structure in C
Structures in C defines the group of contiguous (adjacent) fields, such as records or control blocks. A structure is a collection of variables grouped together under a single name. It provides an elegant and powerful way for keeping related data together.
Structures in C defines the group of contiguous (adjacent) fields, such as records or control blocks. A structure is a collection of variables grouped together under a single name. It provides an elegant and powerful way for keeping related data together.Description:
In this tutorial you will see how pointer is used with structure. This is a very important example because all data-structure program work on this principle.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
struct record
{
char name[20];
int roll;
};
struct record r,*p;
void main()
{
p=&r;
clrscr();
printf("\nEnter the name\n");
scanf("\n%s",&p->name);
printf("\nEnter the roll no\n");
scanf("%d",&p->roll);
printf("\n%s",p->name);
printf("\n%d",p->roll);
}
Code Description:
p=&r assign the address of object to p
*p allow the pointer to access the objects
*p.roll is same as p->roll like used in example.
Output: